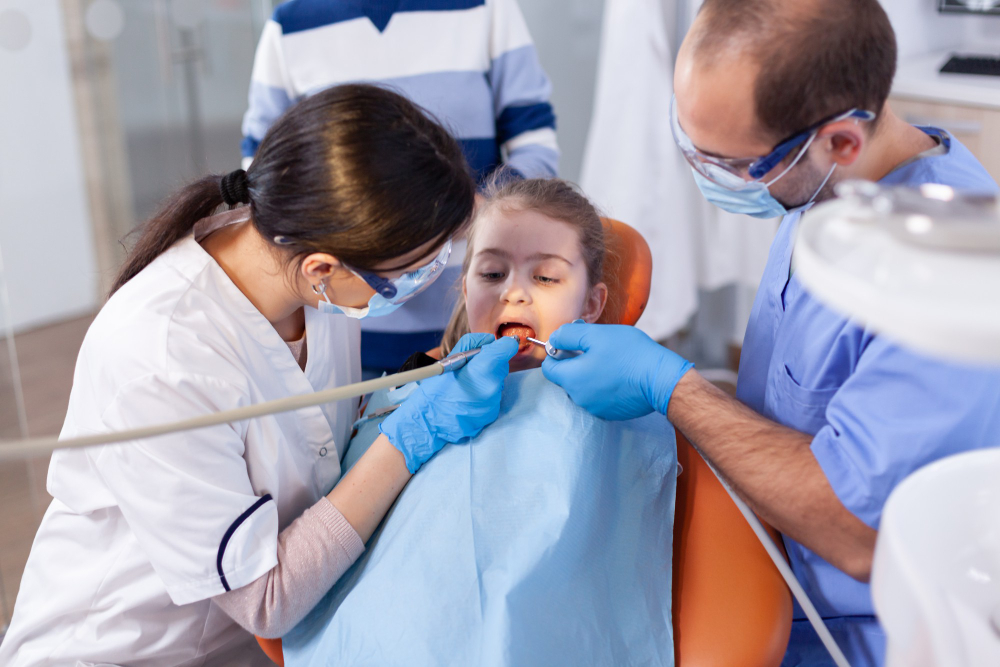
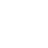
Dental anxiety is a common concern among children, making dental visits a challenging experience for both parents and dental professionals. In such cases, sedation dentistry emerges as a valuable solution. It helps alleviate children’s fear and anxiety, ensuring they receive the necessary dental care without unnecessary stress. But what exactly do dentists use to sedate children safely? In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of sedation techniques and medications commonly used in pediatric dentistry to ensure a comfortable and anxiety-free dental experience for kids.
The Importance Of Pediatric Dental Care
Proper dental care during childhood is crucial for maintaining oral health throughout life. Neglecting dental issues in childhood can lead to more significant problems in adulthood. However, many children develop dental anxiety or phobia, which can result from a variety of factors, including the fear of pain, unfamiliarity with dental procedures, or a traumatic previous experience. Sedation dentistry is an essential tool to address these challenges and ensure that children receive the dental care they need.
Types Of Sedation Used In Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric dentists have various options when it comes to sedating children for dental procedures. The choice of sedation method depends on the child’s age, medical history, and the complexity of the dental work required. Here are the primary types of sedation used in pediatric dentistry:
- Nitrous Oxide (Laughing Gas):
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, is a mild form of sedation suitable for children with mild anxiety or nervousness. It is administered through a small mask placed over the child’s nose and provides a sense of relaxation. Nitrous oxide is safe and has minimal side effects, allowing the child to recover quickly after the procedure.
- Oral Sedation:
Oral sedation involves administering medication in the form of a liquid or pill before the dental appointment. This method is ideal for children with moderate anxiety or for longer, more complex procedures. The child may become drowsy but will remain awake and responsive during the procedure. Common medications used for oral sedation in children include midazolam and diazepam.
- Intravenous (IV) Sedation:
Intravenous sedation is a stronger form of sedation that is typically reserved for children with severe dental anxiety or those requiring extensive dental work. A pediatric anesthesiologist or trained dentist administers the medication through an IV line. This method induces a deeper state of relaxation or even unconsciousness, depending on the dose. IV sedation allows for complex dental procedures to be performed without the child experiencing discomfort or anxiety.
- General Anesthesia:
General anesthesia is the deepest form of sedation and is typically reserved for the most complex dental cases or children with severe developmental issues or disabilities. Under general anesthesia, the child is completely unconscious and unaware of the dental procedure. A specialized team of anesthesiologists and dental professionals administers and monitors the anesthesia throughout the procedure to ensure the child’s safety.
Medications Used In Pediatric Sedation Dentistry
The medications used in pediatric sedation dentistry are carefully chosen to ensure safety and effectiveness. Let’s delve deeper into some of the commonly used medications:
- Benzodiazepines:
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that induce relaxation and reduce anxiety. They are often used for oral sedation in children. Common benzodiazepines used include midazolam (Versed) and diazepam (Valium). These medications have a mild amnesic effect, helping children forget the details of the procedure.
- Propofol:
Propofol is a potent intravenous sedative often used in general anesthesia for children. It provides rapid sedation and a quick recovery time. It’s administered by an anesthesiologist who closely monitors the child’s vital signs throughout the procedure.
- Nitrous Oxide:
Nitrous oxide is a safe and effective inhaled sedative that is administered through a mask over the child’s nose. It is used for its mild sedative and analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. Nitrous oxide has a rapid onset and offset, allowing for precise control during the procedure.
- Sevoflurane:
Sevoflurane is a volatile inhalation anesthetic often used in pediatric general anesthesia. It is delivered through a specialized mask and helps maintain a state of unconsciousness during the procedure. Its advantage lies in its quick elimination from the body, minimizing post-procedural grogginess.
Safety And Monitoring
The safety of children undergoing sedation dentistry is of utmost importance. Pediatric dentists and anesthesiologists are trained to provide a safe and controlled environment during dental procedures involving sedation. Here are some safety measures and monitoring techniques employed:
- Pre-procedure Assessment: A thorough evaluation of the child’s medical history, current health, and any medications they may be taking is conducted before administering sedation. This helps identify any potential risks or contraindications.
- Continuous Monitoring: During sedation, the child’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, are continuously monitored. This ensures early detection of any adverse reactions.
- Pediatric Anesthesiologist: In cases of deep sedation or general anesthesia, a pediatric anesthesiologist with specialized training in caring for children is often involved to administer and monitor the anesthesia.
- Emergency Preparedness: Dental facilities offering sedation dentistry for children are equipped with emergency equipment and medications to respond to any unforeseen complications swiftly.
Sedation dentistry for children plays a crucial role in ensuring that young patients receive the dental care they need without experiencing anxiety or discomfort. Various sedation methods and medications are available to cater to the diverse needs of children with different levels of dental anxiety or those requiring complex dental procedures.
It is essential for parents to discuss their child’s specific needs and concerns with the pediatric dentist, allowing them to make an informed decision regarding the most appropriate sedation method. With proper precautions, monitoring, and the use of safe and effective medications, sedation dentistry can transform dental visits from fearful experiences into positive ones, promoting lifelong oral health for children.